Out Of This World Tips About Why Is 4-wire Better Than 2-wire

Unraveling the Mystery
1. The Core Question
Ever wondered why some electrical setups use four wires while others only need two? It's not just engineers showing off their wire-stripping skills, there's actually a pretty important reason behind it. Think of it like choosing between a bicycle and a car: both can get you from point A to point B, but one is clearly better suited for certain situations. The same applies to wiring!
The key difference boils down to how power is delivered and how sensitive the equipment is to voltage fluctuations. Imagine you're trying to dim the lights in your living room. With a simple 2-wire setup, the dimming might cause other appliances on the same circuit to flicker or act strangely. A 4-wire setup, on the other hand, can minimize these issues and provide a more stable and predictable power supply. It's like having a dedicated lane on the highway for your electricity!
The part of speech we should focus on when discussing "Why is 4-wire better than 2-wire" is adjective. We are comparing the qualitative aspects of two systems. We want to dive into what makes four-wire systems superior, focusing on characteristics like stability, reliability, and performance. Think "more stable," "more efficient," "more reliable," "less susceptible," and "safer."
So, while simplicity has its advantages (like easier installation and potentially lower costs), the benefits of a 4-wire system often outweigh those of a 2-wire system, especially when dealing with sensitive electronics or high-power appliances. But let's delve a little deeper into these advantages, shall we?
2 And 4 Wire Testing What's The Difference?
The Technical Details
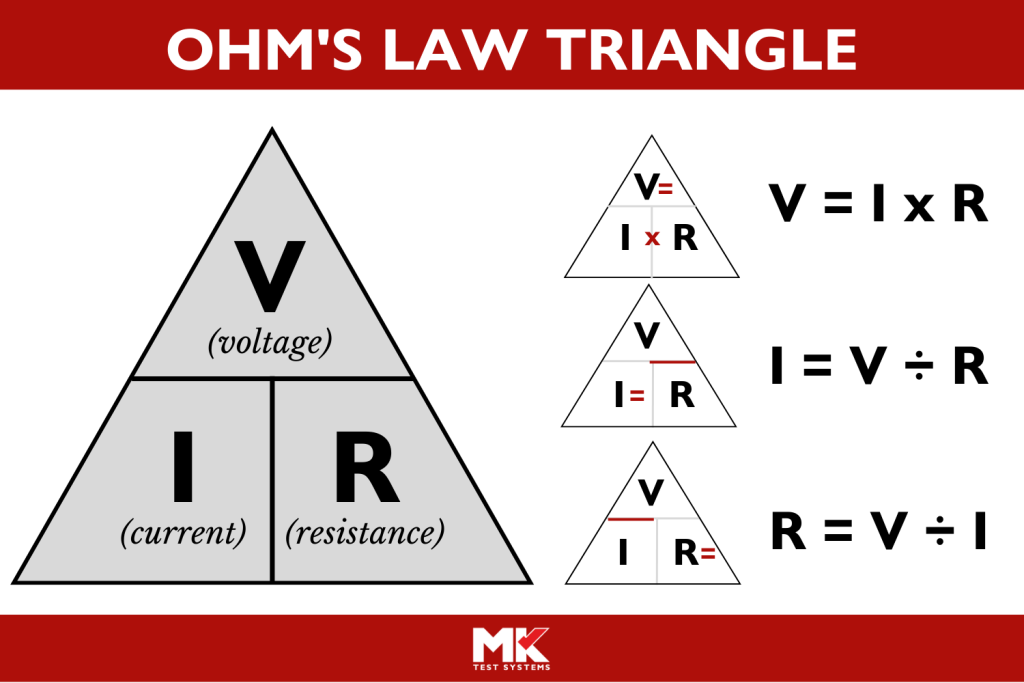
2. Diving into Voltage Drop and Neutral Wires
Let's get slightly technical (but I promise to keep it entertaining!). One of the biggest problems in electrical circuits is voltage drop. As electricity travels through a wire, it loses some of its "oomph" due to resistance. This can cause lights to dim, motors to run sluggishly, and sensitive electronics to malfunction. Think of it like trying to drink a milkshake through a very long and narrow straw you're not going to get the full milkshake experience!
In a 2-wire system, the same wire carries both the supply current and the return current. This increases the voltage drop, especially over longer distances. A 4-wire system, on the other hand, typically includes a separate neutral wire. This allows for a more stable voltage and reduces the voltage drop, ensuring that your appliances receive the power they need to operate correctly. Consider it like having two straws, one for sipping and one for exhaling much easier!
Moreover, the neutral wire in a 4-wire system provides a dedicated return path for unbalanced loads. What does that mean, you ask? Imagine having a perfectly balanced scale. A 2-wire system is like trying to balance the scale with weights that are constantly shifting. A 4-wire system is much better at handling unbalanced loads, ensuring a more stable and reliable power supply. This is especially important in modern homes with a variety of electronic devices, from computers and TVs to refrigerators and washing machines.
In essence, a dedicated neutral wire acts as a "buffer" or a "shock absorber," smoothing out the voltage and current flow. This not only protects your equipment from damage but also improves its performance. And who doesn't want their electronics to perform at their best?
I E And U Designations On Wiring Diagram For Guages Friday F
Applications
3. From Homes to Industries
So, where do you typically find 4-wire systems in action? Well, they're commonly used in modern homes, especially for circuits powering sensitive electronics or high-power appliances. Think about your kitchen appliances refrigerators, ovens, microwaves these often benefit from a 4-wire setup. The same goes for home theater systems, computers, and other devices that are sensitive to voltage fluctuations.
Beyond residential applications, 4-wire systems are widely used in commercial and industrial settings. Data centers, hospitals, and factories rely on stable and reliable power supplies to keep their operations running smoothly. In these environments, even a small voltage fluctuation can have catastrophic consequences, leading to data loss, equipment damage, or even safety hazards. A 4-wire system provides the extra layer of protection needed to minimize these risks.
Another common application is in three-phase power distribution. Three-phase power is often used in industrial settings to power large motors and other heavy machinery. A 4-wire three-phase system provides a neutral wire in addition to the three phase wires, allowing for a more balanced and efficient distribution of power. This is particularly important in factories and other facilities with high power demands.
Furthermore, electric vehicle (EV) charging stations are increasingly employing 4-wire systems, particularly for Level 2 and DC fast charging. These systems provide a more stable and reliable power supply, which is crucial for ensuring efficient and safe charging of electric vehicles. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the use of 4-wire systems in charging infrastructure will only become more prevalent.
Safety First
4. Grounding and Protection
While performance and reliability are important, safety is paramount when it comes to electrical systems. And in this area, 4-wire systems often offer advantages over 2-wire systems. One key aspect is grounding. A 4-wire system typically includes a dedicated ground wire, which provides a low-resistance path for fault currents to flow back to the source. This helps to quickly trip circuit breakers or fuses, preventing electrical shocks and fires.
In a 2-wire system, the ground wire may not be as robust or as effectively connected, which can increase the risk of electrical hazards. A dedicated ground wire in a 4-wire system provides a much more reliable and consistent grounding path, improving the overall safety of the electrical system. It's like having a dedicated escape route in case of an emergency!
Another safety advantage of 4-wire systems is their ability to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). EMI can interfere with the operation of sensitive electronic devices, causing them to malfunction or produce inaccurate readings. A well-designed 4-wire system can minimize EMI by providing a dedicated return path for currents, reducing the amount of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the wires.
Furthermore, using a 4-wire configuration can aid in detecting wiring errors more easily. By having separate neutral and ground wires, any unintended current flow in the ground wire becomes immediately apparent, indicating a potential fault. This allows for quicker identification and correction of wiring issues, minimizing the risk of electrical accidents and equipment damage.

Cost and Complexity
5. Is it Always the Best Choice?
Okay, so 4-wire systems sound pretty great, right? More stable, more reliable, safer... But there are also some potential drawbacks to consider. The biggest one is cost. A 4-wire system generally requires more materials (i.e., more wire!), which can increase the overall installation cost. Also, installing a 4-wire system can be more complex than installing a 2-wire system, requiring more time and expertise.
So, is it always the best choice? Not necessarily. In some cases, a 2-wire system may be perfectly adequate and more cost-effective. For example, for simple lighting circuits or low-power appliances, a 2-wire system may be sufficient. The key is to carefully evaluate the specific needs of the application and weigh the benefits of a 4-wire system against the cost and complexity.
The decision often comes down to risk tolerance. If you're willing to accept a slightly higher risk of voltage fluctuations or electrical hazards in exchange for lower costs and simpler installation, then a 2-wire system might be a viable option. However, if you prioritize stability, reliability, and safety above all else, then a 4-wire system is likely the better choice.
Ultimately, it's a balancing act. Consider the equipment you're powering, the environment it's in, and your budget. Consulting with a qualified electrician can help you determine the best wiring solution for your specific needs, ensuring that you get the performance, reliability, and safety you need without breaking the bank.

FAQ
6. Q
A: Not so fast! It's generally not recommended to simply replace a 2-wire outlet with a 4-wire outlet without upgrading the wiring itself. You need to have a dedicated ground wire available in the circuit to properly ground the 4-wire outlet. If you don't have a ground wire, you're just adding the appearance of safety without the actual protection. Consult with a licensed electrician before making any changes to your electrical wiring.
7. Q
A: Electrical codes vary by location, but generally, modern codes require a 4-wire system (including a dedicated ground wire) for most new installations and renovations. However, there may be some exceptions for certain types of circuits or existing wiring systems. Always check with your local electrical codes to ensure that your wiring meets the requirements.
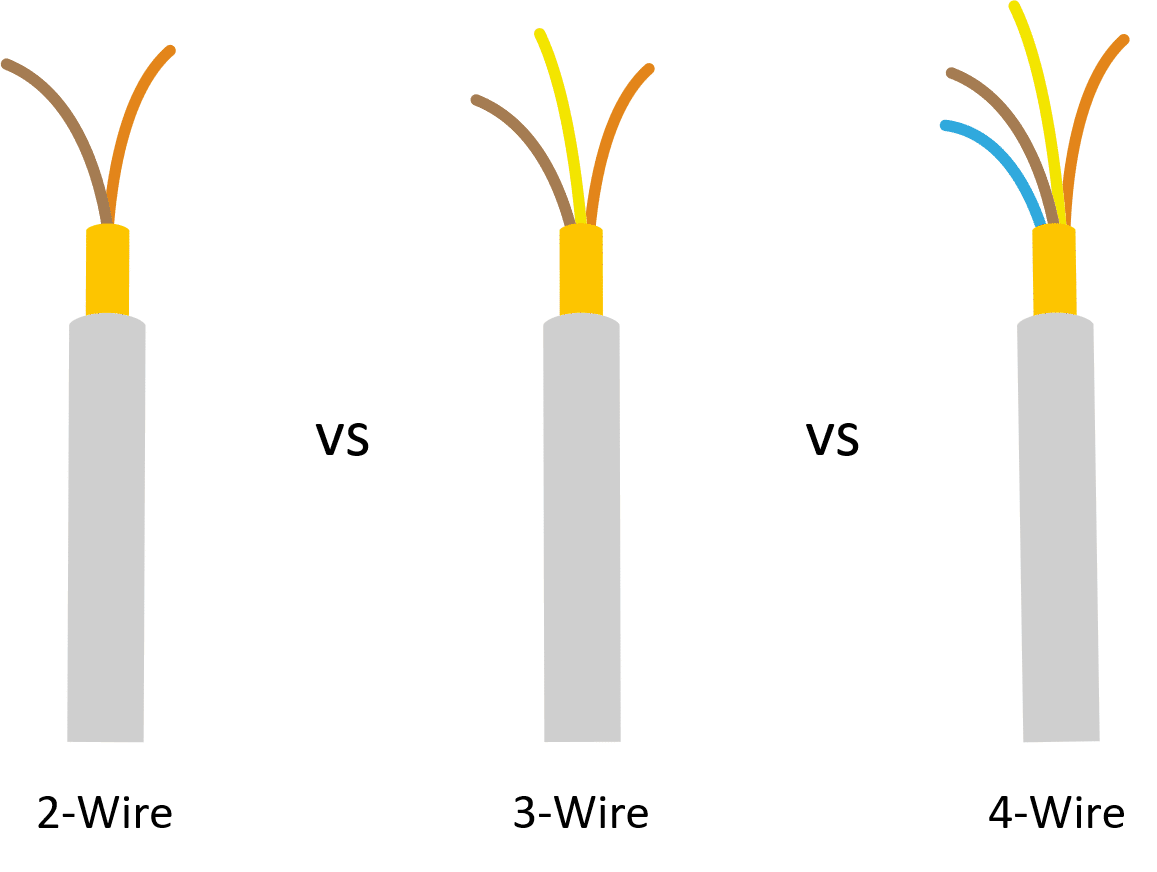
8. Q
A: The easiest way to tell is to look at your electrical outlets. A 2-wire outlet will typically have two slots, while a 4-wire outlet will have three (two slots and a round grounding hole). However, keep in mind that some older homes may have 2-wire outlets that have been replaced with 3-prong outlets without actually having a ground wire. It's best to have an electrician inspect your wiring to determine the type of system you have and ensure that it's safe and up to code.