Recommendation Tips About Is There A Difference Between ECU And ECM

Decoding the Engine Brain
1. Unraveling the Mystery
Ever popped the hood of your car and wondered about all those little black boxes humming away? Two terms you might stumble upon are ECU and ECM. Are they different? The same? Used interchangeably? Well, let's clear up the confusion once and for all! Think of it like trying to tell the difference between your identical twin cousins — they look alike, but their personalities might be worlds apart.
The short answer? Things have evolved. Back in the day, the distinction was a bit clearer. But as cars got smarter (and a tad more complicated, let's be honest), the lines blurred. What used to be separate functions are often integrated into a single unit these days. So, while there was a difference, modern automotive engineering often throws that neat little distinction out the window.
Imagine a world where your smartphone only handled calls, and you needed a separate device for browsing the internet. That's kind of how ECUs and ECMs used to be. One handled specific tasks, while the other managed something else. But now? Your phone does everything! The same goes for many modern car computers.
So, if you hear someone using ECU and ECM interchangeably, don't be too quick to correct them (unless you're trying to win a trivia night, then go for it!). They're likely referring to the same thing — the central processing unit of your car's engine.

What Is The Difference Between ECM And ECU?
Delving into the Historical Context
2. A Glimpse into Automotive History
Let's take a trip down memory lane to understand where the confusion originated. Traditionally, the ECM, or Engine Control Module, was primarily responsible for managing the engine's core functions. This included controlling fuel injection, ignition timing, and idle speed. Think of it as the engine's dedicated manager, ensuring everything ran smoothly within the combustion chamber.
The ECU, or Engine Control Unit, on the other hand, often encompassed a broader range of functions. It might have controlled the ECM, but it also could have been responsible for other engine-related systems, such as emissions control or even some aspects of the transmission. It was more like the overall supervisor of the engine's operations.
Think of it this way: the ECM was the chef, meticulously preparing the engine's "meal" (combustion). The ECU was the restaurant manager, overseeing the chef and ensuring the kitchen ran efficiently, taking into account factors like customer preferences (driving style) and resource availability (fuel quality).
But, as technology advanced, manufacturers started combining these functions into a single, more powerful unit. This integration streamlined the system, reduced complexity, and improved overall performance. This is why the terms are often used interchangeably today.

Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Purpose And Function YouTube
Modern Automotive Systems
3. The Age of Integrated Control
Today, in many modern vehicles, the ECU and ECM functions are integrated into a single computer. This unit handles a wide array of tasks, from managing the engine's performance to controlling the transmission, anti-lock braking system (ABS), and even some aspects of the vehicle's stability control system. It's essentially the brain of the entire powertrain.
This integration allows for more sophisticated control strategies and improved communication between different vehicle systems. For example, the engine control unit can communicate with the transmission control unit to optimize gear shifts based on driving conditions and engine load. This results in smoother acceleration, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced overall driving experience.
The move toward integrated control units also simplifies diagnostics and repair. Instead of having to troubleshoot multiple separate modules, technicians can often diagnose issues through a single interface. This saves time and reduces the likelihood of misdiagnosis.
While some specialized applications might still use separate ECUs and ECMs, the trend is clearly toward integration. So, unless you're working on a classic car or a highly specialized vehicle, it's safe to assume that the terms ECU and ECM are referring to the same thing: the main computer that controls your engine.
.jpg)
Aniket Shah & Alexander Witt Ppt Download
Keyword Term
4. Understanding the Grammar
The keywords "ECU" and "ECM" are both nouns. They also function as abbreviations for "Engine Control Unit" and "Engine Control Module," respectively. Understanding their grammatical role is crucial because it helps clarify how they function within sentences and how they relate to other parts of the automotive system.
For instance, you might say, "The ECU controls the fuel injectors." Here, "ECU" is the subject of the sentence, performing the action of controlling. Similarly, you could say, "The mechanic replaced the faulty ECM." In this case, "ECM" is the direct object of the verb "replaced." Knowing they are nouns helps frame them in technical discussions and diagnostic procedures.
In more complex contexts, these terms are often used attributively, acting like adjectives to describe other nouns. For example, " ECU programming" or " ECM calibration." In these phrases, "ECU" and "ECM" modify the nouns "programming" and "calibration," indicating that these processes are related to the engine control system.
Recognizing that ECU and ECM are nouns and abbreviations ensures clarity in automotive writing and communication, preventing misunderstandings and promoting accurate information exchange among professionals and enthusiasts alike.

Know Your Car Difference Between PCM, ECM, BCM And TCM
When to Worry (and When Not To!)
5. Troubleshooting Tips
Okay, so when should you actually be concerned about whether it's an ECU or an ECM issue? Honestly, unless you're a seasoned mechanic working on older vehicles with distinct systems, probably not that much. The more important thing is what your car is doing (or not doing!), rather than which module is at fault.
Common symptoms of a failing ECU/ECM (remember, they're likely the same thing!) include a check engine light, difficulty starting, poor fuel economy, stalling, and unusual engine behavior. If you experience any of these, it's time to get your car checked out by a qualified mechanic. They have the tools and expertise to diagnose the problem accurately, regardless of whether they call it an ECU or an ECM.
Don't fall into the trap of assuming you need a new ECU/ECM based solely on internet searches or forum posts. These modules are complex and expensive, and replacing one without proper diagnosis is a costly mistake. A thorough diagnostic process, using specialized equipment and software, is essential to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
Ultimately, whether it's referred to as an ECU or ECM, the goal is the same: to ensure your engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Focus on getting the problem diagnosed and repaired correctly, rather than getting hung up on the terminology.
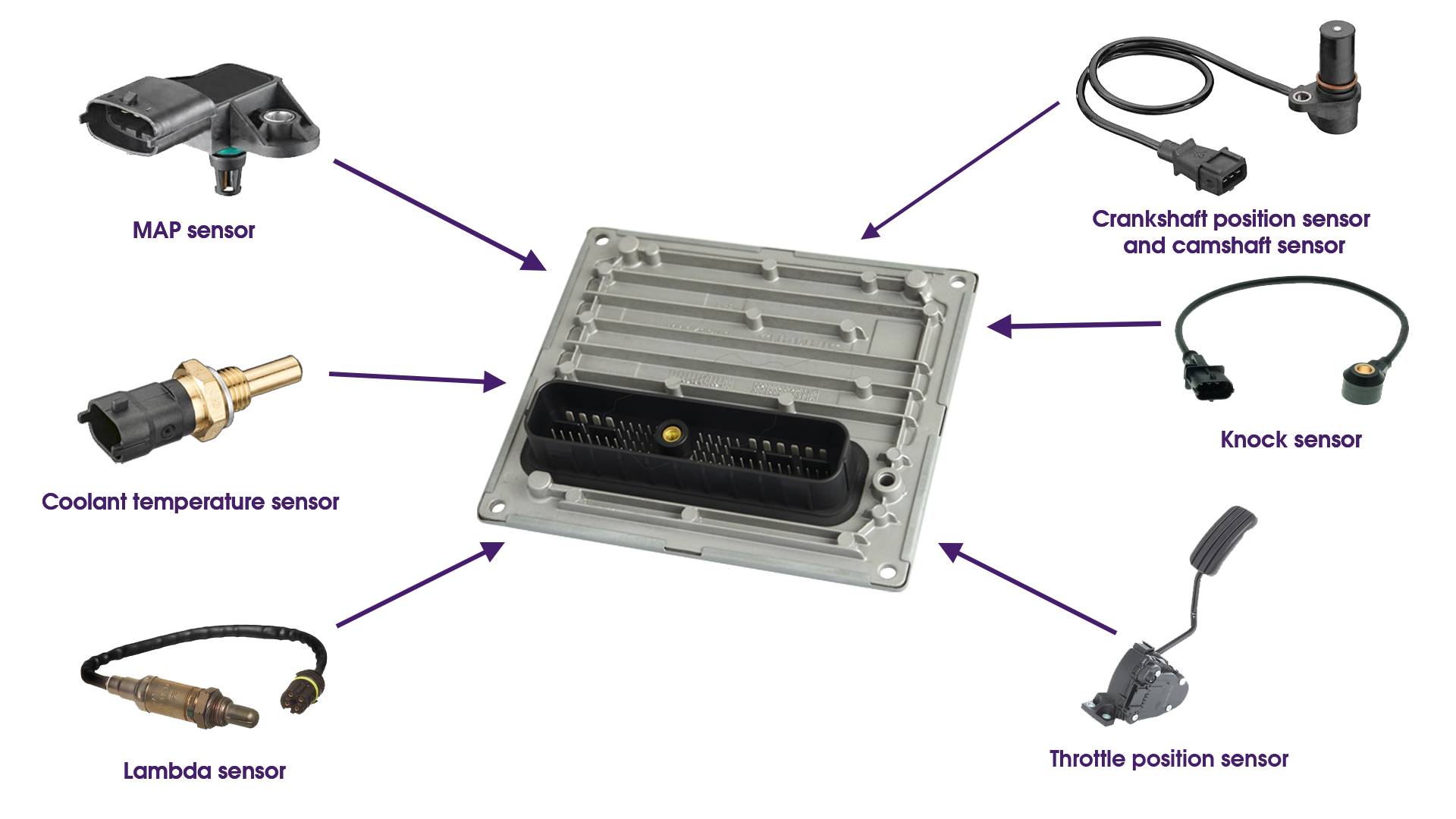
What Exactly Is An Ecu In Electric Vehicle Jenni Norine
FAQ
6. Quick Answers to Common Queries
Still scratching your head? Let's tackle some frequently asked questions:
Q: Can I replace my ECU/ECM myself?A: While technically possible in some cases, it's generally not recommended unless you have extensive automotive repair experience and the necessary diagnostic tools. ECUs/ECMs often require programming and calibration to match your specific vehicle, which can be complex and requires specialized software.
Q: How much does it cost to replace an ECU/ECM?A: The cost can vary widely depending on the make and model of your vehicle, as well as the complexity of the system. Generally, you can expect to pay anywhere from a few hundred to several thousand dollars for a new ECU/ECM and installation.
Q: Will a bad ECU/ECM affect my car's emissions?A: Absolutely. A malfunctioning ECU/ECM can lead to increased emissions due to improper fuel combustion and other issues. This can cause your car to fail an emissions test and potentially result in fines or other penalties.
Q: How can I tell if my ECU/ECM is failing?A: Common signs include a check engine light, difficulty starting, poor fuel economy, stalling, and unusual engine behavior. However, these symptoms can also be caused by other issues, so it's important to have a professional diagnosis performed.
Q: Are there aftermarket performance ECUs/ECMs available?A: Yes, there are aftermarket ECUs/ECMs designed to improve engine performance. These modules often offer advanced tuning capabilities and can be customized to optimize your engine for specific modifications. However, installing an aftermarket ECU/ECM can void your vehicle's warranty.