Sensational Info About What Is Cheaper To Run, 3-phase Or Single-phase

Why Is 3 Phase Better Than Single » Wiring Work
Understanding Electrical Systems
1. Exploring the Basics
Ever wondered about the electricity powering your home versus that powering a large factory? It boils down to how the electrical power is delivered. We're going to delve into single-phase and three-phase systems, which are the two main players in this arena. Think of single-phase as your reliable, everyday electrical setup, perfect for most household needs. Now, three-phase is the beefier cousin, designed for heavy-duty applications like industrial machinery and large commercial buildings. But the big question is: when it comes to keeping those electricity bills down, what is cheaper to run, 3-phase or single-phase?
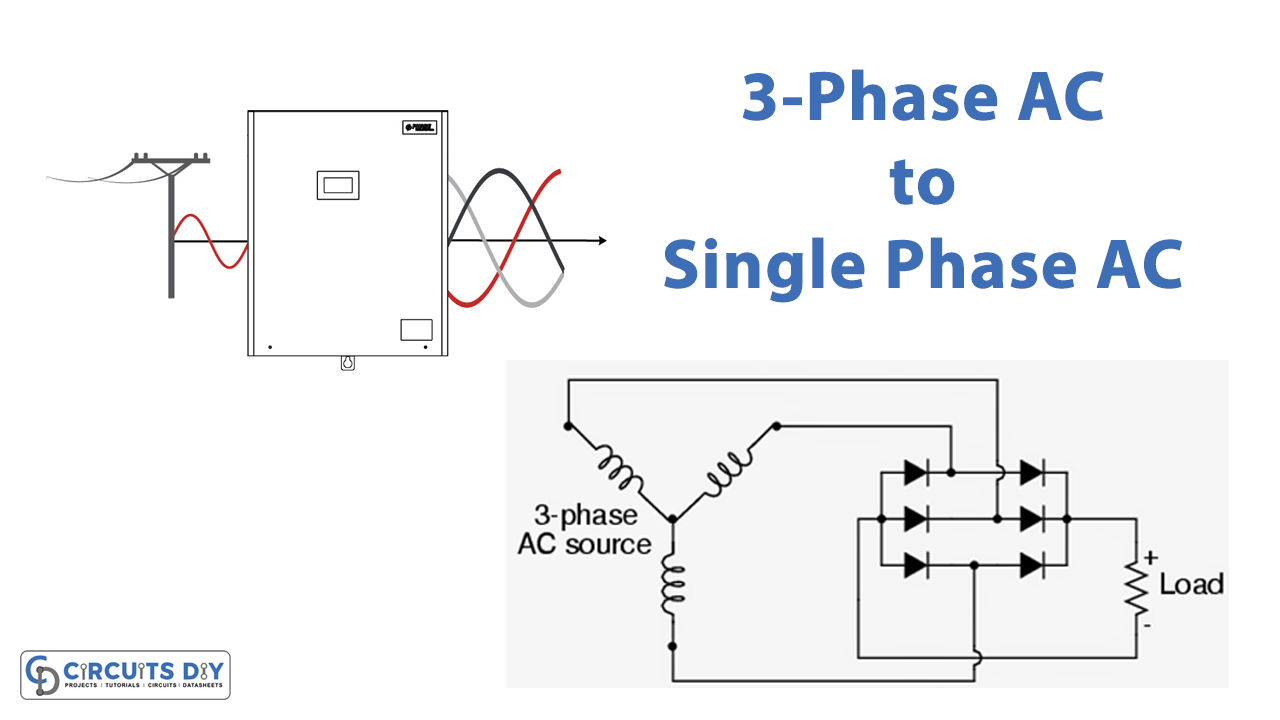
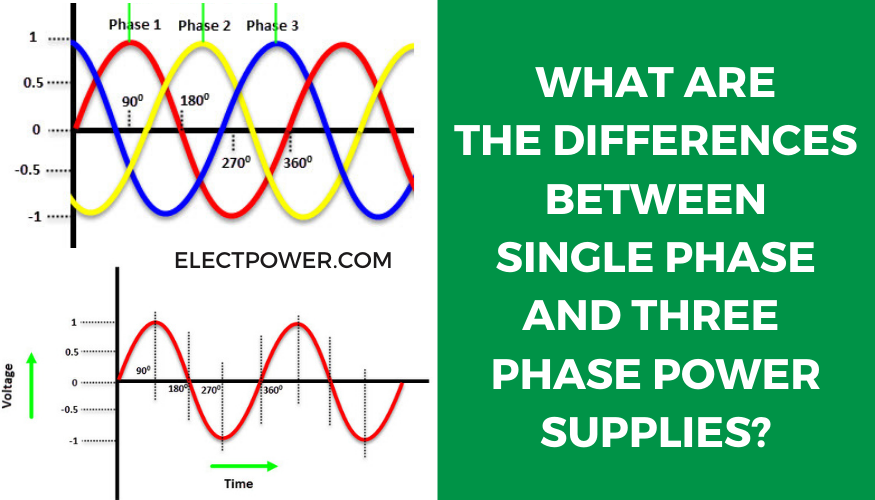
To really understand the cost differences, we need to look under the hood (so to speak) of each system. Single-phase power, as the name suggests, uses a single alternating current (AC) voltage. It's simple, straightforward, and generally sufficient for lower power demands. Three-phase, on the other hand, employs three AC voltages, each offset by 120 degrees. This arrangement provides a smoother, more consistent power delivery, making it ideal for demanding loads.
The key difference lies in the efficiency and power capacity. Three-phase systems can deliver more power with smaller wires compared to single-phase. This translates to potential savings in infrastructure costs for large-scale applications. However, the initial setup for three-phase can be more expensive. So, the "cheaper to run" aspect isn't always a simple yes or no answer; it depends heavily on the specific application.
Think of it like choosing a car: a compact single-phase system is like a fuel-efficient sedan for daily commutes, while a robust three-phase system is like a powerful truck built for hauling heavy loads. Both have their place, and the right choice depends on your particular needs and budget. Lets dive deeper into those factors.
Single Phase To Three Digital Conversion, 40 OFF
Cost Factors
2. Initial Investment Matters
Okay, let's talk brass tacks. Initially, installing a three-phase system is almost always going to be more expensive than a single-phase system. You're dealing with more complex equipment, specialized wiring, and often, the need for a qualified electrician experienced in three-phase setups. The cost of transformers, circuit breakers, and other components are also higher for three-phase.
So, if you're building a new home or a small business with relatively low power needs, sticking with single-phase is usually the more budget-friendly option. It's simpler to install, readily available, and perfectly adequate for running lights, appliances, and basic machinery. The upfront savings can be significant.
However, don't just look at the initial cost. Think about the long game. If you anticipate needing more power down the line, upgrading from single-phase to three-phase later can be a real headache (and a wallet-drainer). That's where planning and future-proofing become essential.
Essentially, it's a trade-off. Short-term savings with single-phase versus potential long-term benefits with three-phase. It's like deciding whether to buy that slightly cheaper, less efficient appliance now or investing in a more energy-efficient model that will save you money over time.
Can A 3 Phase Motor Run On Single Power
Operational Efficiency
3. Powering Up Productivity
Now, let's get to the heart of the matter: operational costs. This is where three-phase often shows its muscle. Three-phase motors, commonly used in industrial settings, are generally more efficient than their single-phase counterparts. They run smoother, last longer, and require less maintenance. That increased efficiency translates directly into lower electricity bills over the long run.
Furthermore, three-phase systems can handle much heavier loads without straining the electrical grid. This is crucial for businesses with large machinery, such as manufacturing plants or commercial kitchens. A single-phase system might struggle to power these heavy-duty appliances, leading to voltage drops, overheating, and even equipment failure. This can also influence what is cheaper to run, 3-phase or single-phase.
Imagine a woodworking shop. A small, hobbyist shop with a few basic power tools might be perfectly fine with single-phase. But a large-scale operation with heavy-duty saws, planers, and dust collection systems will almost certainly benefit from the reliability and efficiency of three-phase power.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to use single-phase or three-phase boils down to power requirements. If you need to power large, demanding equipment regularly, the improved efficiency of three-phase can easily offset the higher initial cost over time. It's like choosing between a bicycle and a motorcycle — both get you from point A to point B, but one is better suited for covering long distances and carrying heavy loads.

How To Run A 3Phase Motor On SinglePhase Supply Using VFD?
Real-World Examples
4. Applying the Knowledge
Let's look at some practical examples to solidify our understanding. In a typical residential setting, single-phase power is the standard. It's more than enough to run your lights, appliances, air conditioner, and even a small electric vehicle charger. The cost of installing three-phase in a home is rarely justified, unless you have extremely unusual power needs.
On the other hand, consider a large commercial building with multiple tenants, elevators, and a complex HVAC system. Three-phase power is almost certainly essential. It provides the capacity and stability needed to keep everything running smoothly without overloading the system. The higher initial cost is easily absorbed by the operational efficiencies and the ability to handle large power demands.
Another good example is a data center. These facilities require massive amounts of power to run servers and cooling equipment. Three-phase power is the go-to choice for data centers because it can handle the high power density and ensure reliable operation. Power outages can be catastrophic for a data center, so the robustness of three-phase is a critical advantage.
So, the context is key. A small bakery might get by with single-phase, but a large food processing plant definitely needs three-phase. A home office is perfectly happy with single-phase, but a skyscraper relies on three-phase to keep the lights on and the elevators running. Understanding your specific power needs is the first step in making the right choice. So knowing what is cheaper to run, 3-phase or single-phase is important.

How To Run Three Phase Motor Single Connection A 3
Making the Right Choice
5. Evaluating Your Needs
Okay, so you've learned about the differences between single-phase and three-phase power, the upfront costs, the operational efficiencies, and some real-world examples. Now, how do you actually decide which one is right for you? There are several factors to consider.
First, assess your current and future power needs. How much power do you actually use? What kind of equipment do you need to run? Are you planning to expand your operations in the future? Get a clear picture of your power requirements. You can consult with an electrician or electrical engineer to conduct a load calculation, which will give you a precise estimate of your power demands.
Second, compare the upfront costs of installing each type of system. Get quotes from qualified electricians for both single-phase and three-phase installations. Factor in the cost of equipment, wiring, and any necessary upgrades to your electrical panel. Be sure to get detailed breakdowns of the costs so you can compare them apples-to-apples. And make sure to check the what is cheaper to run, 3-phase or single-phase?
Third, consider the long-term operational costs. How much will it cost to run your equipment on each type of system? Will three-phase power save you money on electricity bills over time due to its higher efficiency? Factor in the cost of maintenance and potential downtime. You might need to estimate the lifespan of your equipment and calculate the total cost of ownership over that period.
Finally, don't be afraid to seek professional advice. Talk to an experienced electrician or electrical engineer. They can assess your specific situation and provide you with tailored recommendations. They can also help you navigate any local regulations or permitting requirements.

FAQ
6. Answers to Your Electrical Inquiries
Let's address some frequently asked questions to clear up any remaining confusion.
Q: Can I convert single-phase power to three-phase power?
A: Yes, it's possible to convert single-phase to three-phase using a device called a rotary phase converter or a static phase converter. However, these converters can be expensive and may not be as efficient as a native three-phase system. It's generally better to install a true three-phase system if you require significant three-phase power.
Q: Is three-phase power dangerous?
A: Three-phase power is not inherently more dangerous than single-phase power. However, it operates at higher voltages and currents, so it's essential to follow proper safety procedures when working with it. Always hire a qualified electrician to install and maintain three-phase systems.
Q: Will three-phase power improve the performance of my equipment?
A: If your equipment is designed to run on three-phase power, it will generally perform better and more efficiently than on single-phase power (even with a converter). Three-phase motors run smoother, last longer, and require less maintenance. It all boils down to what is cheaper to run, 3-phase or single-phase with the needed type of equipment.