Glory Tips About How To P2P Connection

P2P Network Architecture Windows Server 2019 Administration
Unlocking the Secrets of P2P Connections
1. What Exactly Is This P2P Thing?
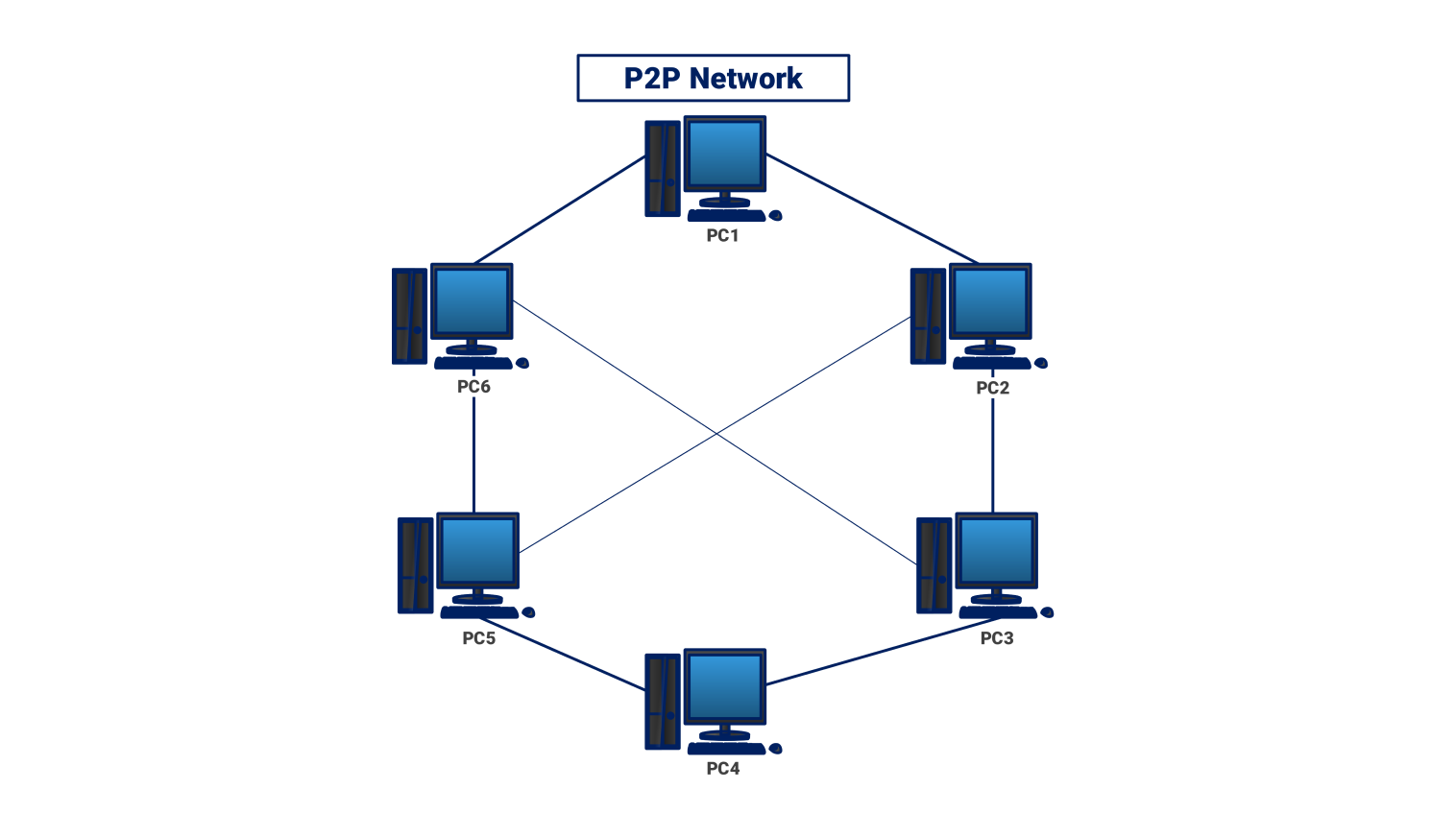
Ever wondered how files magically appear on your computer from seemingly nowhere? Or how you can stream videos from someone across the globe without a central server getting involved? Chances are, you've stumbled into the world of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) connections. It's like a digital handshake between computers, cutting out the middleman. Instead of downloading something from a big, official server, you're grabbing bits and pieces from other users just like you! Think of it as a digital potluck; everyone brings something to the table.
Now, before you picture rogue computers swapping top-secret files in the dead of night, let's clear something up. P2P isn't inherently bad. It's just a technology. Like a hammer, it can be used to build houses or, well, do other less constructive things. Legitimate uses abound, from collaborative software development to scientific research and even good old file sharing where everyone has the right permissions, of course.
Imagine a group project where everyone can directly contribute and see each other's changes instantly — that's P2P in action! It's about distributed power, decentralization, and empowering individual users. This can lead to faster speeds, greater resilience against server outages (because there is no central server!), and a more democratic internet. But like any good thing, understanding how it all works is key.
So, how does this digital potluck work? Each "peer" in the network acts as both a client (downloading files) and a server (uploading files). Think of it as everyone being simultaneously the chef and the diner. This constant sharing of resources creates a vibrant ecosystem where data can flow efficiently and quickly. Plus, with enough peers participating, the network becomes incredibly robust, able to withstand even significant disruptions.

Intro. To Computer Lecture 19 Client Server And Peer (P2P
Setting Up Your Own P2P Connection
2. Getting Your Ducks in a Row
Ready to dive in and establish your own P2P connection? Great! First, you'll need to pick your weapon, or rather, your application. There are numerous P2P platforms and protocols out there, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some are designed for specific tasks, like sharing large files, while others offer more general-purpose functionality. Popular options include BitTorrent, which is widely used for downloading large files, and direct connect clients for LAN file sharing.
Next, think about security. Because you're directly connecting to other users, it's crucial to protect your privacy and prevent unauthorized access to your system. Make sure your firewall is properly configured and up to date. Consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to encrypt your traffic and hide your IP address. Its a bit like wearing a disguise in the digital world; it helps keep your online activities private.
Now, for the nitty-gritty. Most P2P applications require some configuration to work optimally. This typically involves setting up port forwarding on your router. Port forwarding is like telling your router, "Hey, when someone knocks on this specific port number, send them directly to this computer on my network." Without it, incoming connections might get blocked, preventing you from sharing files or participating in the network.
Finally, before you start sharing files willy-nilly, make sure you understand the legal and ethical implications. Copyright infringement is a serious issue, and downloading or sharing copyrighted material without permission can land you in hot water. Always ensure you have the rights to share the files you're distributing. It's always better to be safe than sorry.
Network Diagram For P2P
The Upsides and Downsides
3. Weighing the Pros and Cons
Like any technology, P2P has its advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, it can be incredibly efficient for sharing large files, especially when a central server is overloaded or unavailable. Think of trying to download the latest video game on release day; P2P can significantly reduce download times by tapping into the collective bandwidth of other users who already have the game.
Another major benefit is decentralization. By distributing data across multiple users, P2P networks are more resilient to censorship and single points of failure. If one peer goes offline, the network can continue to function without interruption. This makes it a powerful tool for promoting freedom of information and resisting attempts to control online content. This also makes the network strong, as you don't have to worry if the main server is down.
However, there are also downsides to consider. Security risks are a primary concern, as connecting directly to other users exposes your system to potential vulnerabilities. Malware, viruses, and other nasty surprises can spread quickly through P2P networks. Thats why its essential to have a robust antivirus program and to be careful about the files you download.
Also, the anonymity afforded by P2P networks can be a double-edged sword. While it can protect privacy, it can also be exploited by individuals engaged in illegal activities. This makes it challenging to regulate P2P networks and prevent the distribution of copyrighted material or other illegal content. So, like any powerful tool, it comes with responsibilities.

Network Architecture Client Server Model Peer To Or P2p
P2P in the Real World
4. Beyond the Downloads
While P2P is often associated with file sharing, its applications extend far beyond that. Many modern technologies rely on P2P principles to improve performance, scalability, and security. For example, some content delivery networks (CDNs) use P2P to distribute video content more efficiently. By caching content on users' computers, they can reduce the load on central servers and deliver a smoother streaming experience.
Another exciting application is in the realm of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin, for example, relies on a P2P network to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. This decentralized approach eliminates the need for a central authority, making the system more secure and resistant to manipulation. Its like having a global ledger thats maintained by everyone, not just a single bank.
Even social media platforms are experimenting with P2P technologies to improve performance and reduce costs. By distributing content directly between users, they can bypass central servers and deliver a faster, more responsive experience. This is particularly useful in areas with limited internet infrastructure, where traditional server-based solutions may be unreliable.
Furthermore, scientific research is increasingly leveraging P2P for distributing large datasets and facilitating collaboration. Researchers can use P2P networks to share data and computational resources, enabling them to tackle complex problems more efficiently. It's a bit like a virtual lab where scientists from all over the world can work together seamlessly, without being limited by geographical boundaries.

Staying Safe and Smart
5. Rules to Live By
Now that you know the ins and outs of P2P connections, let's talk about staying safe and smart. First and foremost, always use a reputable antivirus program and keep it up to date. Scan all downloaded files before opening them to prevent malware infections. Think of it as a digital vaccine; it helps protect your system from harmful viruses.
Secondly, be mindful of your privacy settings. Many P2P applications allow you to control how much information you share with other users. Consider limiting the amount of personal data you expose to the network. Its a bit like keeping your blinds closed; it prevents unwanted eyes from peering into your digital life.
Thirdly, use a VPN to encrypt your traffic and hide your IP address. This adds an extra layer of security and privacy, making it more difficult for others to track your online activities. It's like putting on a mask; it helps protect your identity in the digital world.
Finally, be aware of copyright laws and respect intellectual property rights. Only download and share files that you have the legal right to access. Ignorance of the law is no excuse, and copyright infringement can have serious consequences. Its better to err on the side of caution and ensure youre not violating anyones rights.

FAQ
6. Still Scratching Your Head?
Let's tackle some of the most common questions about P2P connections.
7. What's the difference between P2P and a regular download?
With a regular download, you're getting the file from a single server. With P2P, you're getting pieces of the file from multiple users simultaneously. This can be much faster, especially for popular files.
8. Is P2P always illegal?
No! P2P technology itself is legal. It's how it's used that can sometimes be illegal. Sharing copyrighted material without permission is against the law.
9. Can P2P slow down my internet?
Yes, if you're uploading files while downloading or doing other bandwidth-intensive activities, it can affect your internet speed. Most P2P clients allow you to limit your upload speed to prevent this.
10. How do I know if a P2P file is safe to download?
There's no foolproof way to guarantee a file is safe, but you can check the file's hash (a unique fingerprint) against a trusted source or use a reputable antivirus program to scan it before opening.